close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media

A micro coaxial cable helps send data and signals in small spaces. It has a thin size, usually between 0.5mm and 2.0mm. This lets you put it inside small devices. The cable bends easily and works well with high-frequency signals. It keeps data safe and steady. Micro coaxial cables are better than standard ones when space is tight. You see them in things like KEL TMC01-51S V-By-One EPD shielded cable and Fakra B antenna extension cables.
The micro coaxial cable market is growing faster than the standard coaxial cable market. You can see this in the table below:
| Cable Type | Market Size (2025) | Projected Size (2035) | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micro Coaxial Cables | USD 2,538.9 million | USD 4,500 million | 5.9% |
| Standard Coaxial Cables | USD 35,558.39 million | USD 46,413.74 million | 2.7% |
Micro coaxial cables are very small. They measure between 0.5mm and 2.0mm. This size makes them great for tight spaces. Devices like smartphones and medical tools use them.
These cables bend easily. They do not lose signal when bent. This is important for portable electronics.
Micro coaxial cables use strong materials. These materials can handle heat. They keep the signal clear. This helps the cables work well in many places.
Picking the right connectors is important. Good connectors keep signals strong. They also help fit cables into small designs.
More people are using micro coaxial cables now. This shows they are important in new technology. They are needed for fast data transmission.
Micro-coaxial cables are very small. Their outer diameter is between 0.22 mm and 1.16 mm. This is much less than standard coaxial cables like RG174, which are about 2.79 mm wide. The tiny size lets you put these cables in tight places. You can use them inside smartphones, tablets, and medical devices.
Outer diameter range for micro-coaxial cables: 0.22 mm to 1.16 mm
Outer diameter for standard coaxial cables (RG174): 2.79 mm
Micro-coaxial cables use American Wire Gauge sizes from 50AWG to 32AWG. These thin wires are found in electronics and medical tools. Every millimeter matters in these devices. The slim shape saves space and keeps things light.
Micro-coaxial cables fit well in small devices. Their tiny size makes them bend easily and move through tight spots.
The materials in micro-coaxial cables help them work in tough places. Makers use strong silver-plated or tinned-copper alloys for the conductors. These metals fight heat and last longer. The insulation is important too. Polyethylene, PTFE, and FEP are used a lot. These materials protect the cable and keep signals clear.
Here is a table showing the most common materials and their temperature resistance:
| Material | Type | Maximum Temperature Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | Conductor | 100°C |
| Copper-clad steel | Conductor | 100°C |
| Silver-plated copper | Conductor | 200°C (short-term 250°C) |
| Tin | Conductor | 150°C (rarely 200°C) |
| Polyethylene | Insulation | 85°C |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Insulation | 250°C |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene propylene | Insulation | 200°C |
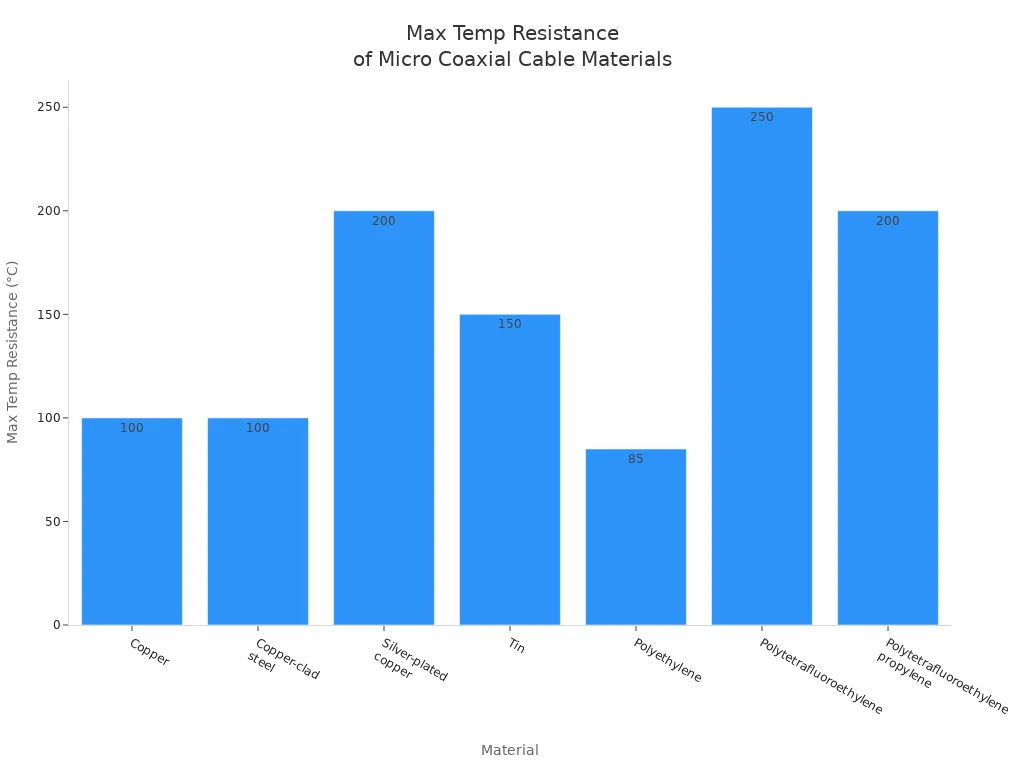
These materials help the cable work when temperatures change. Micro-coaxial cables stay strong and do not break easily. You can trust them in medical and industrial devices. They work well in many different conditions.
You need cables that bend without losing signal. Micro-coaxial cables are very flexible. The smallest bend is six times the cable’s outer diameter. You can twist and turn the cable in small devices. It will not get damaged.
Flexibility is needed for portable electronics and medical tools.
Cables must bend and move but still keep good signals.
The dielectric material inside the cable is important. Foam PE, PTFE, and FEP are used often. These materials lower the dielectric constant. This means less signal loss. You get better signals, especially at high frequencies.
| Dielectric Material | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Foam PE | Reduces dielectric constant, lower signal loss | High-frequency applications |
| PTFE | Low dielectric constant, excellent thermal stability | Aerospace, military, high-frequency RF |
| FEP | Low signal loss, high temperature resistance | Flexible environments requiring durability |
Lower dielectric constants mean less signal loss. This is good for long cables and fast data.
PTFE works well for gigahertz uses. You see it in advanced electronics.
Tip: Pick micro-coaxial cables with good dielectric materials. This keeps your data safe and your devices working well.
Inside every micro coaxial cable, there are several key parts. Each part helps the cable work well in your devices.
The center conductor sends signals. You need this part for clear data.
The dielectric core wraps around the center conductor. It keeps the signal safe and helps stop signal loss.
The outer metallic jacket has many strands. This part gives a path for ground current and blocks outside noise.
Another jacket covers the cable. It adds more insulation and protects from interference.
You can use the center conductor for power signals. It can send DC supply, and the outer shield can be used for DC return. This design lets you send both data and power in small devices.
When you look at micro-coax cable assemblies, you see these parts work together. They keep signals strong and steady. The thin shape lets you put cables in tight spaces, like inside smartphones or medical tools. The KEL TMC01-51S V-By-One EPD shielded cable is a good example. It uses 51 pins and 40 coaxial lines. This shows you can fit many signals in a small space.
Here is a simple list of how each part helps:
The center conductor sends signals well.
The dielectric core stops signal loss and insulates.
The outer metallic jacket blocks electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The extra jacket makes the cable stronger and safer.
Shielding and insulation help micro coaxial cables work well in busy places. Good shielding blocks electromagnetic interference (EMI) and keeps your data safe.
| Shielding Type | Description | Shielding Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Phase3 Series | Helically wrapped Ag-plated Cu first shield with flat braid | -110dB |
| EMC Series | Armored version with metallic armor and additional metallic braid | -125dB |
Strong shielding stops outside electromagnetic fields from messing up your signals. It stops reflections, crosstalk, and noise. You get better data and fewer mistakes.
Grounding the cable sheath lowers EMI.
Routing cables the right way stops electromagnetic coupling.
Using shielded cables with strong protection keeps signals clear.
Insulation materials are important too. In medical and aerospace places, you often see PTFE, FEP, and PFA. These materials handle high heat, chemicals, and can be cleaned easily. They also keep signal loss low, which helps data move fast and stay correct.
| Material | Properties |
|---|---|
| Fluoropolymers | Handles high heat, low friction, flame retardant, strong dielectric strength |
| PFA | Low dielectric constant, very thin walls, good for tiny wires |
| FEP | Saves money, handles high heat, works well electrically |
| ETFE | Stronger, resists scratches |
| Silicone Rubber | Very flexible, good for places needing bendy cables |
You see these insulation choices in micro-coax cable assemblies for medical and aerospace tools. PTFE gives you steady signals and low loss. FEP is easier to use and still handles heat. PFA is tough and works well with electricity.
Some micro coaxial cables use special materials like ARACON® fiber for shielding. This fiber is light and covers over 90%, giving great EMI protection. Silicon dioxide is another insulation choice. It has low loss, fast speed, and resists heat and radiation.
If you compare micro coaxial cables to standard coaxial cables, you see some differences:
| Feature | Coaxial Cable | Micro Coaxial Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two coaxial cylinders with insulation/shielding | Strip-shaped conductors with insulation and ground plane |
| Insulation Layer | Between conductor and shielding | Between conductors and ground plane |
| Overall Dimensions | Bigger because of two cylinders | Smaller because of micro design |
You get benefits from the small size and strong shielding in micro-coax cable assemblies. These features let you use the cables where space is tight and performance matters.
There are different connectors made for micro coaxial cables. These connectors help you attach cables to devices safely. They also keep signals strong and clear. Micro coax connectors come in many shapes. Each type works best for certain jobs.
u.fl connectors are used in wireless gadgets and small electronics. You find them in laptops, tablets, and IoT devices. They handle high-frequency signals and fit in tiny spaces.
mhf connectors are also very small. You use them in cell phones, GPS units, and drones. Their design lets you connect quickly and get steady signals.
Fakra connectors, like those in Car Radio Antenna Extension Cable Fakra B, have colors for car systems. They make sure antennas and radios stay connected well.
Here is a table that shows connector types and where you use them:
| Connector Type | Application Area | Features |
|---|---|---|
| u.fl connectors | Wireless modules, IoT | Ultra-small, high-frequency |
| mhf connectors | Mobile, GPS, drones | Compact, easy to integrate |
| Fakra B | Automotive, radio antennas | Color-coded, robust |
| Micro coax connectors | Medical, industrial, consumer | Shielded, customizable |
Tip: Pick connectors that fit your device’s size and signal needs. Small connectors save space and let you change your design easily.
When you put micro coaxial cables in small devices, you need to think about a few things. You want low signal loss and strong power handling. The cables should work well and be safe. Good shielding stops unwanted noise. Easy assembly saves time.
Low loss keeps signals clear.
Strong power handling stops overheating.
Reliability and safety protect your device.
Shielding blocks noise.
Easy assembly helps you work faster.
Micro coaxial cables bend and twist easily. This helps in devices with moving parts, like laptop hinges or drone cameras. You see this in the KEL TMC01-51S V-By-One EPD shielded cable. It has 51 pins and 40 coaxial lines for fast data. The cable comes in lengths from 100mm to 500mm. It has 50Ω impedance and custom choices for pins and shielding.
You may face problems when building devices. Making things smaller is hard. Keeping signals strong in tight spaces is important. The cables must work well in heat or vibration.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Miniaturization | You need to make cables and connectors fit in small spaces. |
| Signal Integrity | You must keep signals strong in crowded setups. |
| Reliability under Extreme Conditions | Cables and connectors must work in tough places. |
You often make interconnects smaller, lighter, and faster. You change designs for bending and twisting, especially in moving devices. Custom choices, like in Car Radio Antenna Extension Cable Fakra B, let you pick cable length, connector type, and shielding for your needs.
Note: When picking micro coax connectors, make sure they fit your device and the place you use them. Custom options help you meet special needs.

Micro coaxial cables are used in many medical tools. They help machines like imaging equipment and endoscopy systems work well. These cables need to keep signals strong and bend easily. They must block outside interference and follow safety rules. In surgery, micro coaxial cables send data quickly. This helps doctors see images right away. The small size makes devices lighter and more exact. You also find these cables in oximetry and patient monitors. Their layers keep signals clear and steady.
Diagnostic imaging equipment
Endoscopy systems
Medical probes
Oximetry systems
Patient monitoring
Micro coaxial cables make medical devices small and strong. This means better safety and performance.
Micro coaxial cables are used in many electronics you use. Phones, tablets, and laptops need these cables for fast data. The cables fit inside small spaces and send signals quickly. Test equipment also uses micro coaxial cables to keep data correct. In small electronic systems, these cables help you get good connections. The KEL TMC01-51S V-By-One EPD shielded cable is one example. It sends LVDS signals in screens and locks in place for safety.
Smartphones
Tablets
Laptops
Test and measurement equipment
Compact electronic systems
Tip: Use micro coaxial cables for devices that need quick data and small parts.
Micro coaxial cables are found in many industrial machines. They send high-frequency and fast signals. Automated factories use cables like XtendedFlex 178 for robots. These cables bend a lot and last a long time. Aerospace and RF test equipment need micro coaxial cables for strong links and steady signals. Vision systems use these cables to connect cameras to computers with little delay. Fakra B antenna extension cables work in cars and factories for good RF signals.
| Equipment Type | Application Example |
|---|---|
| Automated manufacturing | Robotics, industrial automation |
| Aerospace avionics | Strong connections, low signal problems |
| RF test equipment | Steady signals, good shielding |
| Embedded vision systems | Camera to computer links |
| Automotive | Infotainment, ADAS, antenna extension |
Micro coaxial cables help you make strong and fast industrial machines.
You get lots of good things from micro coaxial cables. They are small and bend easily. This helps you make tiny devices. You still get strong signals. These cables fit in tight spots. They send fast data. Fast data is needed for 5G and IoT. It is also needed for new electronics. You find these cables in medical tools. You see them in cars and home gadgets too. They keep signals clear and steady. If you learn about micro coaxial cables, you can build better technology. Your devices will work well and last longer.
Micro coaxial cables have a much smaller diameter, usually between 0.5mm and 2.0mm. You can use them in tight spaces where regular cables do not fit. They also bend easily and support high-frequency signals.
Yes, you can choose the cable length and connector type. For example, Fakra B antenna extension cables come in lengths from 1.5 cm to 7 m. You can ask for custom connectors to match your device.
You find micro coaxial cables in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and medical devices. They help send fast data and fit inside small spaces. The KEL TMC01-51S V-By-One EPD shielded cable is used for LVDS signals in screens.
Tip: Check your device’s space, signal needs, and connector type. Look for cables with strong shielding and the right length. Ask for custom options if you need a special fit.
